
Rutile, primarily composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), is a fundamental mineral in various industrial applications due to its unique properties and natural abundance. Its widespread occurrence makes rutile a crucial raw material for producing chloride titanium dioxide pigment, which is essential in manufacturing processes for welding electrodes.
Rutile typically forms through the concentration of “heavy mineral sands,” where natural processes like stream and wave action lead to its accumulation. These sands, found in both onshore and offshore deposits worldwide, serve as primary sources for rutile extraction, with a significant portion of global production originating from these abundant mineral sands.
One of rutile’s notable characteristics is its high specific gravity, which facilitates its concentration during mining operations. The TiO2 content in rutile extracted from mineral separation plants consistently exceeds 95%, underscoring its importance in various industrial processes.
In summary, rutile plays a vital role in the industrial landscape, contributing significantly to the production of essential materials like titanium dioxide pigment.
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
Grade : Rutile 95% Guaranteed
| TiO2 | 95% Min |
| SiO2 | 1.2% Max |
| S | 0.003% Max |
Grade : Rutile 92% Guaranteed
| TiO2 | 92% Min |
| SiO2 | 1.5% Max |
| S | 0.005% Max |
Grade : Rutile 92% Guaranteed
| TiO2 | 90% Min |
| SiO2 | 2% Max |
| S | 0.007% Max |
Grade : Leucoxene 88% Guaranteed
| TiO2 | 88% Min |
| SiO2 | 2% Max |
| S | 0.005% Max |
Natural Rutile
Source: Natural rutile is extracted from mineral deposits, primarily found in heavy mineral sands rich in various heavy minerals, including rutile, ilmenite, and zircon.
Composition: It is mainly composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), with minor impurities such as iron oxide (Fe2O3) and other transition metal ions.
Characteristics: Natural rutile displays a variety of colors, including colorless, white, brown, red, or yellow, depending on impurities present. It may also contain mineral inclusions and exhibit pleochroism.
Uses of Rutile Sand
- Titanium Dioxide Pigment Production
- Welding Electrodes
- Refractory Materials
- Titanium Metal Production
- Optical Coatings
- Ceramics
- Plastics and Paper
Advantages of Rutile Sand
- High Titanium Dioxide Content
- Stability in Extreme Conditions
- Corrosion Resistance
- High Refractive Index
- Versatility
- Efficiency in Mining
- Sustainable and Recyclable
Applications
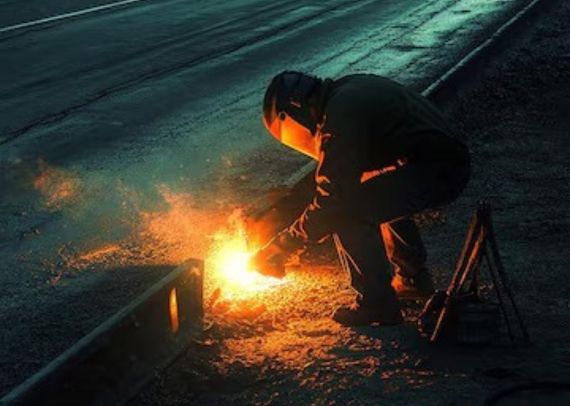


Welding Electrodes:
Rutile is a vital ingredient in welding flux formulations, where it acts as a coating on welding electrodes. This coating stabilizes the arc, enhances weld quality, and protects the molten metal from atmospheric contamination. Rutile-containing fluxes are widely employed in both manual and automated welding processes across various industries.
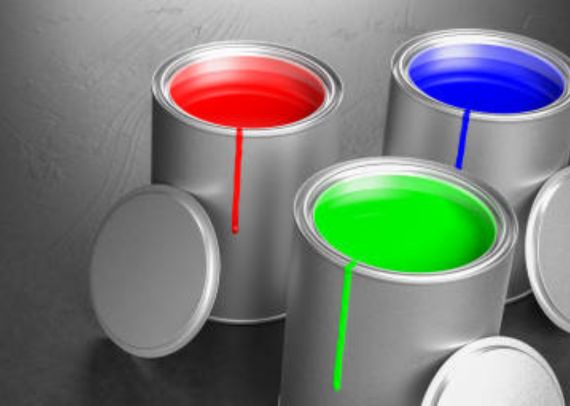
Titanium Dioxide Pigment:
Rutile serves as a primary raw material for producing titanium dioxide pigment. Extracted from rutile through various processing techniques, this pigment is extensively used in manufacturing paints and other materials. Rutile-based titanium dioxide pigments provide exceptional opacity, brightness, and UV resistance, making them essential for numerous applications.


