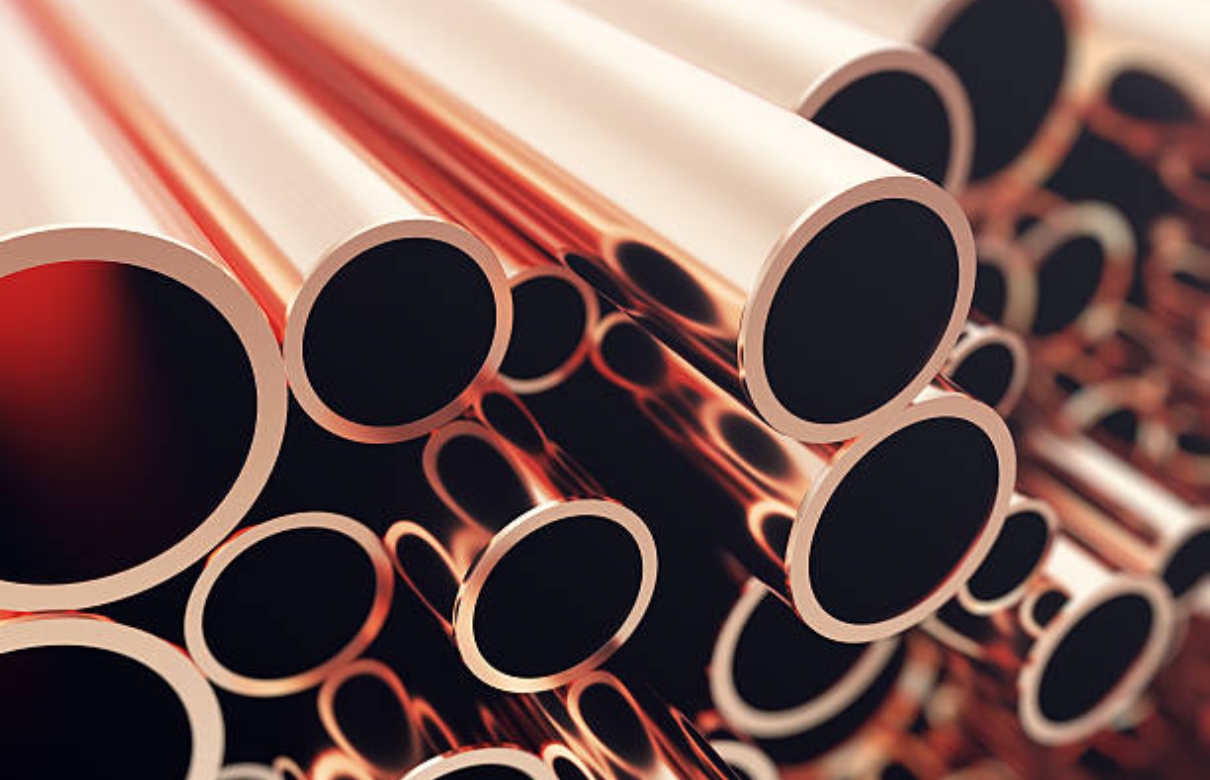

Copper metals are highly versatile and widely used across industries due to their excellent conductivity. As a preferred material for electrical wiring and electronics, copper efficiently conducts electricity, making it crucial in power generation and distribution. Its high thermal conductivity also makes it ideal for heat exchangers and radiators. Additionally, copper’s resistance to corrosion and antimicrobial properties add value in plumbing and sanitary applications, while its durability and aesthetic appeal make it popular for roofing, gutters, and architectural elements.
The metal’s malleability and ductility allow it to be shaped into various forms, from wires to complex components. Copper alloys like bronze and brass are valued for their strength and durability, used in machinery, automotive parts, and decorative items. Furthermore, copper’s recyclability contributes to sustainability, as it can be efficiently reused without compromising quality, supporting a circular economy. These unique properties make copper indispensable in modern infrastructure, technology, and manufacturing.
Uses of Copper
- Electrical Wiring
- Electronics
- Plumbing
- Construction
- Heat Exchangers
- Copper Alloys
- Antimicrobial Applications
Advantages of Copper
- Excellent Conductivity
- Corrosion Resistance
- Malleability and Ductility
- Durability
- Recyclability
- Antimicrobial Properties
- Aesthetic Appeal


